A routine urine culture detects the amount of germs (like bacteria) present in the urine.Once a urine sample is collected, a technician will keep it in conditions where microorganisms can multiply. Normally, no more than a small number of germs will be present in the urine if there's no infection. If a larger number of germs are present, the technician will use a microscope or chemical tests to determine the specific types growing in the culture. The technician also may run tests to determine which medications will be most effective against the microorganism if the doctor diagnoses an infection.

In MedSim simulation the process is mainly divided in to
● Physical Examination
● Chemical Analysis
● Microscopic Examination
Physical Examination
All routine urinalysis should begin with a physical examination of the urine sample. This examination includes assessment of odor, and appearance (color and turbidity).
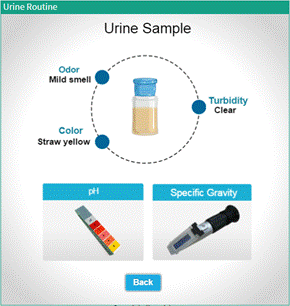
Fig: Tests available in Physical Examination of Urine Sample
|
Physical Examination of Urine |
Procedure |
|
Odor |
Non-pathological, fresh urine has an inoffensive odor. One usually determines the odor of the urine sample by placing one's nose near the orifice of the sample and smell. ● System displays the odor on screen |
|
Appearance (color and turbidity)
|
The color of non-pathological urine varies widely from colorless to deep yellow; the more concentrated the urine, the deeper the color. ● System displays the appearance of urine on screen |
|
pH Test |
● Click on the icon, pH test from the side menu. ● The system will display a urine sample , litmus paper and the pH chart. ● Click and drag the dropper in the urine sample over the litmus paper. ● Observe the color changes of the litmus paper. ● Now, drag the litmus paper near to the color table to find the pH value. ● To return to the main menu, hit “Back”. |
|
Specific gravity |
A hydrometer (urinometer) and a suitable container may be used to determine specific gravity. ● Click on the icon , specific gravity to perform the test. ● The system will display a urine sample and Refractometer. ● Click on the close lid to open it . ● Click and drag the dropper of the urine sample over the open lid. ● Click the lid to close it again. ● The zoomed view of the scale will be displayed.The reading will be based on the specific gravity of the sample. ● Hit "Reset" to redo the experiment anytime. ● To return to the main menu, hit “Back”. |
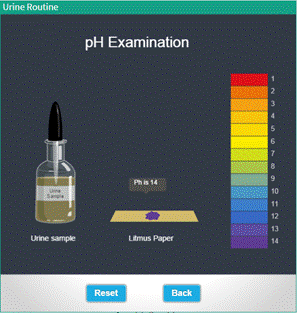
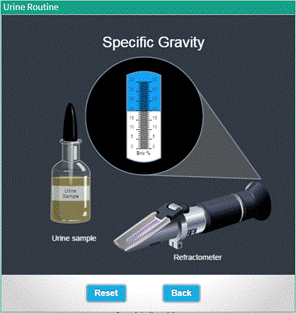
Fig : User interface to test determine the pH and Specific Gravity of Urine Sample
Chemical Analysis
Chemical examination of urine involves the testing of the urine sample chemically for substances that provide valuable information about health and disease. User can perform of the following tests or activity to determine its concentration in the urine sample which is normally not found in the urine and may indicate some disease or another condition.
|
Chemical Analysis of Urine |
Procedure |
|
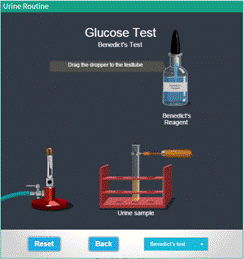
Glucose Test (Benedict's Test) |
● The system will display a test tube containing urine sample, Benedict’s reagent and Bunsen Burner. ● Click and drag the dropper containing Benedict’s reagent near the mouth of the test tube containing urine sample to pour the reagent to the test tube. ● Turn on the burner by clicking the knob. ● Click and drag the test tube to the burner flame. ● Check the chemical changes takes place in the urine sample, ● Click "Reset" Button to redo the experiment ● To return to the main menu, hit “Back”. |
|
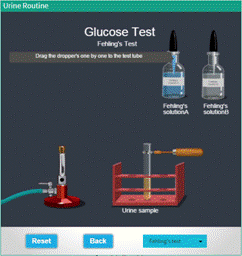
Glucose Test (Fehling's Test) |
● Select the " Fehling's Test" from the drop down menu. ● Click and drag the dropper containing "Fehling's solution A " near the mouth of the test tube containing urine sample to pour the solution to the test tube. ● Click and drag the dropper containing "Fehling's solution B" near the mouth test tube containing of the urine sample to pour the solution to test tube. ● Turn on the burner by clicking on the knob. ● Click and drag the test tube to the burner flame. ● Observe for the chemical changes take place in the urine sample, ● Click "Reset" Button to redo the experiment. ● To return back to the main menu, hit “Back”. |
|
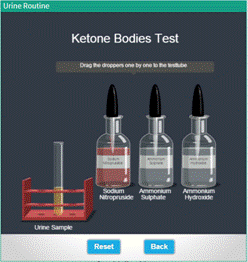
Ketone Bodies Test |
● Click and drag the dropper from "Sodium Nitroprusside" near the mouth of the test tube containing urine sample to pour solution to test tube. ● Click and drag the dropper from "Ammonium Sulphate" near the mouth of the test tube containing urine sample test tube to pour solution to the test tube. ● Click and drag the dropper from "Ammonium Hydroxide" near the mouth of the test tube containing urine sample to pour solution to test tube ● Click on the test tube to shake it gently. ● Observe for the chemical changes takes place in the urine sample. ● Click "Reset" Button to redo the experiment. ● To return to the main menu,hit “Back”. |
|
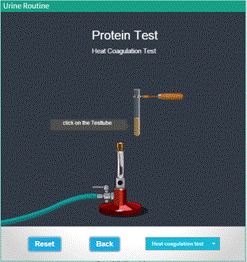
Proteins Test (Heat Coagulation Test) |
● Click on the test tube to hold it near the burner flame . ● Turn on the burner by clicking the knob. ● Observe the chemical changes take place in the urine sample. ● Click "Reset" Button to redo the experiment. ● To return to the main menu,hit “Back”. |
|
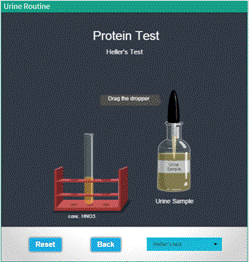
Proteins Test (Heller's test) |
● Select the " Heller's Test" from the drop down menu. ● Click and drag the dropper containing "Urine Sample" near the mouth of the test tube containing concentrated HNO3 to pour urine sample to the test tube. ● Observe for the chemical changes take place in the test tube . ● Click "Reset" Button to redo the experiment. ● To return to the main menu, hit “Back”. |
|
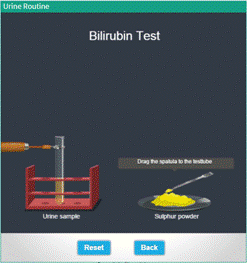
Bilirubin Test |
● Click and drag the spatula containing sulphur powder near the mouth of the test tube containing the urine sample . ● Pour the sulphur powder into the sample. ● Observe the chemical changes takes place in the test tube . ● Click "Reset" Button to redo the experiment. ● To return to main menu, hit “Back”. |
Microscopic Examination
Microscopic Examination of urine sample identifies and counts the type of cells, casts, crystals, and other components, such as bacteria and mucus, that can be present in urine. The activity allows the user to observe the sediments in the sample through the zoomed microscopic view of the urine sample.
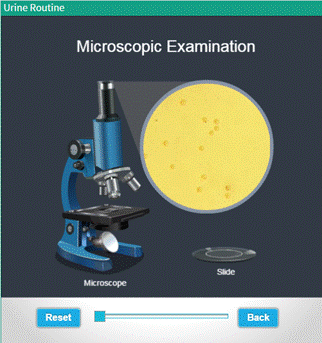
Procedure
● Click and drag the slide containing urine sample to the microscope stage.
● User can see the microscopic view of the urine sample .
● Use "Zoom slider" to adjust the zoomed view.
● Click "Reset" Button to redo the experiment.
● To return to the main menu,hit “Back”.